
Support Squad: Crafting Your Ultimate Recovery Network
Why a Recovery Support System is Essential for Lasting Sobriety A Recovery support system is your network of people and resources that help you maintain sobriety.
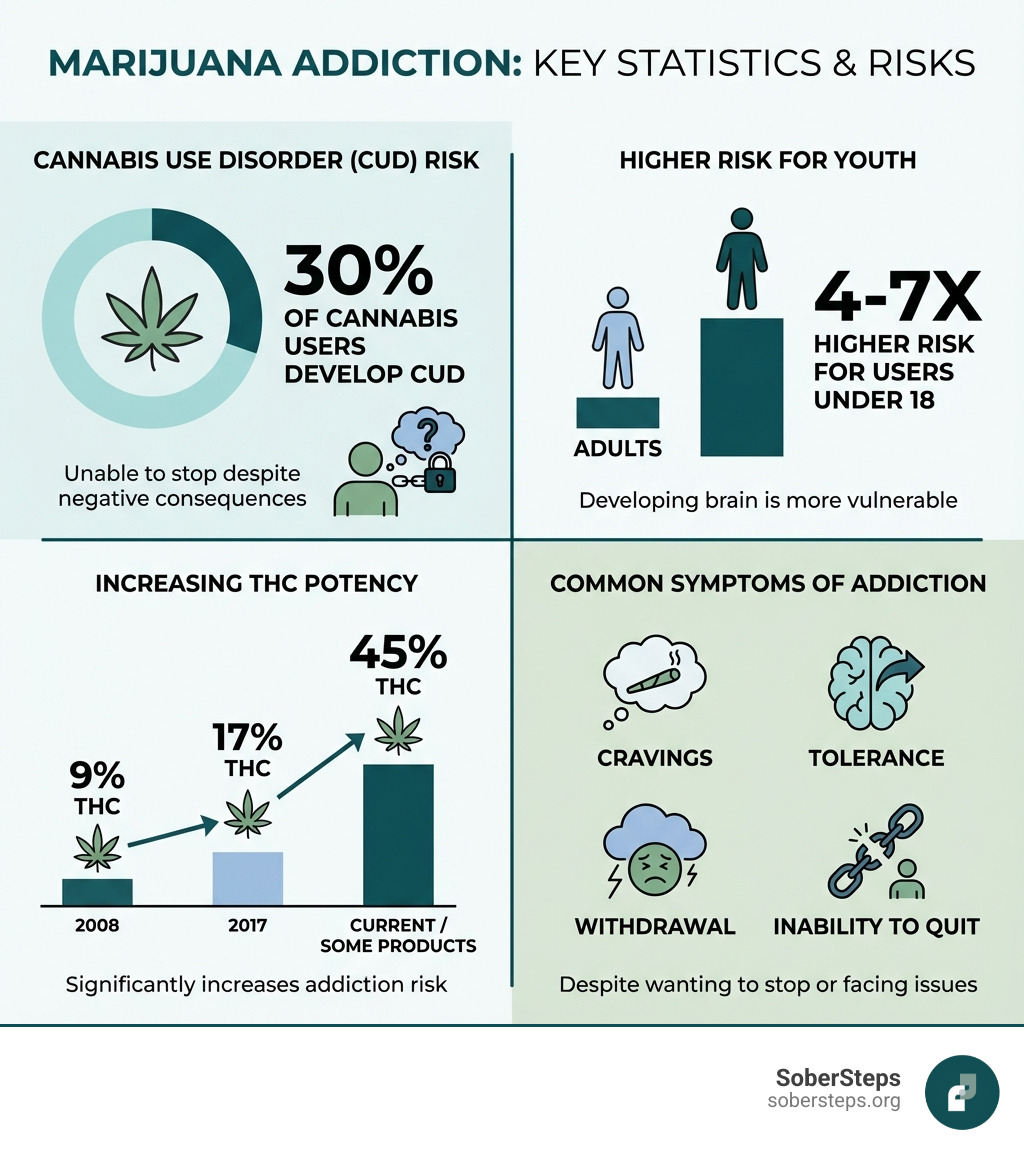
Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment is an increasingly important topic as cannabis use rises. Despite common beliefs, research shows that approximately 3 in 10 people who use cannabis develop cannabis use disorder (CUD), meaning they cannot stop using it even when it causes serious life problems.
Quick Overview:
Cannabis is the most commonly used federally illegal drug in the U.S. With THC concentrations rising from 9% in 2008 to over 17% in 2017—and some products reaching 45% THC—the risk of addiction has grown significantly.
A key distinction exists between recreational use, abuse, and addiction. Not everyone who uses marijuana develops a problem. However, continued use despite negative consequences, an inability to cut back, or withdrawal symptoms upon stopping are signs of cannabis use disorder.
People who begin using cannabis before age 18 are four to seven times more likely to develop CUD than adults. Among daily users, nearly 19% meet dependence criteria.
At Sober Steps, we understand the challenges of marijuana addiction. We have helped countless individuals find confidential, evidence-based treatment for Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment, and we are here to guide you through recovery.
Recognizing the signs of Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment can be difficult, as people often hide their use. However, several indicators can signal a problem.
Behavioral Signs: These include declining performance at school or work, secrecy about use, and possessing paraphernalia (pipes, rolling papers). Individuals may continue using despite negative consequences, try unsuccessfully to quit, and use in risky situations like driving. Other signs are changes in eating patterns (“the munchies”) and stashing cannabis in various places.
Physical Indicators: Physical signs include bloodshot eyes, dry mouth, increased appetite, fatigue, and impaired coordination. A decline in personal hygiene can also occur with chronic use.
Psychological Symptoms: Psychological symptoms include poor concentration, delayed reactions, and impaired judgment. Mood swings, irritability, paranoia, confusion, and memory problems are common. In severe cases, hallucinations or delusions can occur.
Social and Occupational Problems: Socially, a person may withdraw from family and friends, preferring peers who also use. Work or school performance often suffers due to lost motivation. Financial and legal troubles can arise, along with relationship problems and low self-esteem.
Cravings: A strong desire or urge to use cannabis is a hallmark symptom.
Increased Tolerance: Over time, users may need more cannabis or higher THC concentrations to achieve the desired effect.
Giving Up Activities: Important social, occupational, or recreational activities may be given up in favor of using the drug.
Using in Risky Situations: Continuing to use cannabis in physically hazardous situations, such as driving, is a key sign. For more information, refer to the CDC’s guidance on Understanding Your Risk for Cannabis Use Disorder.

Healthcare professionals diagnose Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment using the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). A diagnosis of cannabis use disorder (CUD) requires a pattern of use causing significant impairment, with at least two of the following 11 criteria in a 12-month period:
The severity is determined by the number of criteria met: Mild (2-3), Moderate (4-5), or Severe (6+).
Heavy, frequent users who stop or reduce cannabis use may experience withdrawal. Symptoms typically begin within a week, peak around day 3, and can last up to two weeks, with sleep issues persisting longer.
Common withdrawal symptoms include:
These symptoms can cause significant distress, making it difficult to sustain abstinence without support.
The roots of Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment involve a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and environmental factors.

THC, the psychoactive compound in cannabis, triggers large dopamine surges in the brain’s reward system. Over time, the brain becomes desensitized, requiring more THC for the same effect and creating a compulsive drive for the drug.
Genetics account for 40-60% of the vulnerability to any substance use disorder. A family history of addiction increases the risk for CUD, and specific genes have been linked to higher risk. You can dig deeper into scientific research on CUD and genetics for more detail.
Mental health conditions are closely linked with Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment. About half of those with a mental health condition also have a substance use disorder (a dual diagnosis). Many use cannabis to self-medicate conditions like anxiety or depression, which can worsen the underlying issue and lead to CUD.
Several factors significantly increase the risk of developing CUD:
For adolescents, specific risk factors include parental substance use, poor school performance, and a history of childhood abuse.
The effects of chronic marijuana use are far-reaching, impacting physical health, mental well-being, and social functioning. Understanding these effects is crucial for grasping the full scope of Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment.
The immediate effects of cannabis vary, but chronic use leads to more severe and lasting complications.
| Short-Term Effects (from a single use) | Long-Term Effects (from chronic use) |
|---|---|
| Euphoria, uncontrollable laughter, increased appetite | Addiction (Cannabis Use Disorder) |
| Inattentiveness, forgetfulness, restlessness | Altered brain development (adolescents), lower IQ |
| Tachycardia (increased heart rate), dry mouth | Cognitive impairment (memory, learning, attention), organic neurological dysfunction |
| Conjunctival injection (red eyes) | Poor educational and occupational outcomes |
| Altered time perception, confusion | Chronic bronchitis, increased airway resistance, lung hyperinflation |
| Panic, paranoia, anxiety, hallucinations | Increased risk of head, neck, or throat cancer (from smoking) |
| Impaired motor coordination, poor judgment | Cardiovascular issues (increased risk of stroke, heart attack, arrhythmias) |
| Increased high-risk sexual behaviors | Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome (CHS) |
| Fertility issues (potential effects on both sexes) | |
| Cannabis-induced psychosis, anxiety disorder, sleep disorder |
Cardiovascular Effects: Cannabis temporarily increases heart rate and blood pressure, posing a risk for those with heart conditions. Long-term use is linked to a higher risk of stroke, heart attack, and arrhythmias.
Lung Health: Smoking cannabis exposes the lungs to toxins similar to tobacco smoke. Chronic smoking is linked to respiratory issues like airway inflammation and chronic bronchitis.
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome (CHS): This rare condition in long-term, heavy users causes severe nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. The only cure is to stop using cannabis.
Fertility Issues: Chronic cannabis use may impact fertility in both men and women, potentially affecting sperm in males and ovulation in females.
The impact of Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment extends deeply into long-term health, particularly affecting the developing brain.
Impact on Brain Development in Adolescents: A major concern is the impact on the adolescent brain, which develops until the mid-20s. Early, heavy use can alter brain development, leading to lasting cognitive impairment.
Lower IQ: Studies show that adolescents who use cannabis frequently may experience a permanent decline in IQ.
Impaired Cognitive Function: Chronic use, especially starting in adolescence, can cause persistent and potentially irreversible problems with memory, learning, and attention, affecting performance at school and work.
Poor Educational and Occupational Outcomes: Cognitive and motivational issues from CUD often lead to poor academic and job performance, limiting future opportunities.
Increased Risk of Developing Psychosis: High-potency cannabis use, especially in young people, increases the risk of psychosis and can trigger underlying conditions like schizophrenia. Chronic heavy use can cause delusions and hallucinations that may not resolve after quitting.
The cannabis landscape has changed dramatically, with a significant increase in THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) potency playing a critical role in Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment.
In research samples, average THC concentration nearly doubled from 9% in 2008 to 17% in 2017. Products in some legal markets average 22% THC, with some reaching as high as 45%. This increased potency has profound implications:
The availability of high-potency concentrates (e.g., wax, shatter, extracts) intensifies these risks. These forms deliver highly concentrated THC doses that can speed up the development of tolerance and dependence. Understanding this evolving potency is key to addressing the modern challenges of Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment.
Overcoming Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment is a challenging but achievable journey with the right strategies and support.
While there are no FDA-approved medications for CUD, behavioral therapies are the cornerstone of effective treatment:
We believe in a comprehensive approach. For those needing intensive support, our partners offer structured programs. You can find more info about rehab centers that provide professional guidance.
The path to recovery from Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment is unique for each person, but several elements are consistently helpful:
Recovery is an ongoing process requiring commitment and support. The combination of behavioral therapy, supportive care, and a strong support system offers the best path to lasting sobriety.
We often hear many questions about Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment. Let’s address some of the most common ones.
Yes, marijuana can be both.
Supporting a loved one with Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment is challenging but invaluable. Here are some steps:
You cannot force someone to change, but you can offer consistent support and encourage them to seek professional help.
Yes, recovery from Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment is absolutely possible. With effort and professional support, many people overcome CUD and lead fulfilling, cannabis-free lives.
Recovery often involves:
With the right tools and dedication, lasting recovery is achievable.
We’ve explored the signs, causes, effects, and treatments for Marijuana Addiction: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatment. We’ve seen how rising THC potency amplifies risks, especially for young and frequent users. While addiction can feel isolating, recovery is a reality for many.
Understanding the problem is the first step. Recognizing the signs, acknowledging the causes, and seeking help without shame are vital. Addiction is a treatable health condition, not a moral failing.
At SoberSteps, we help individuals and families steer the complexities of addiction. Our confidential, anonymous online resource connects people to treatment providers across the United States. We believe everyone deserves access to quality care and a chance to build a healthier life.
If you or someone you care about is struggling, don’t wait. Take the first step towards a brighter future.

Why a Recovery Support System is Essential for Lasting Sobriety A Recovery support system is your network of people and resources that help you maintain sobriety.

Connect with online addiction recovery support groups. Explore diverse types, find support, and start your recovery journey virtually.

Understand addiction as a treatable brain condition. Explore effective addictions treatment options, therapies, and find your path to recovery.
For anyone seeking help for addiction for themselves or a loved one calls to Sober Steps are completely confidential and available 24/7.
Please note: any treatment center listed on our site that receives calls is a paid advertiser.
Calls to a specific treatment center’s listing will be connected directly to that center.
Calls to our general helpline will be answered by treatment providers, all of whom are paid advertisers.
By calling the helpline, you agree to our terms and conditions. These calls are free of charge and carry no obligation to enter treatment. Neither Sober Steps nor anyone answering your call receives a commission or fee based on your choice of treatment provider.
If you’d like to explore additional treatment options or connect with a specific rehab center, you can browse our top-rated listings, visit our homepage, or call us at (844) 491-5566. You may also contact us for further assistance.